了解ansible
FuqiangWang
大部分是摘录性的内容,不是一篇完整的思考并融合的结果,仅存之
Ansible是干啥的?(Simple Intro)
Ansible is an IT automation tool. It can configure systems, deploy software, and orchestrate more advanced IT tasks such as continuous deployments or zero downtime rolling updates.
照我说,tmd就是一个可以针对多台机器执行命令的工具,作为国王的你(控制机),只要发号施令, 命令就可以分发到你的子民(目标机)那里执行啦! 至于这个过程中, 授权啦, 通信信道啦, 各种细节,就是ansible帮助打理的地方了,具体有哪些细节值得称道,我们后面慢慢道来…
安装(How to install)
哥用的是mac, 有homebrew这个神器,所以,最简单的安装方法就是:
$ brew install ansible
如果安装过程中出现错误,比如什么东西下载失败之类,请翻墙后再试。
如果想要玩的超前一些(on the blooding edge), 可以直接:
$ git clone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git $ cd ./ansible $ source ./hacking/env-setup
更多细节参考http://docs.ansible.com/intro_installation.html, 不扯那么多了~
装完了,设置ANSIBLE_HOSTS环境变量, 让它指向某个配置文件(叫inventory file)1, 其中将配置目标机器等各种信息,详情后述…
TIP : 可以在命令执行过程中通过-i参数指定使用哪个inventory file,比如
ansible all -i hosts -m shell -a ..., 可以通过版本控制系统来管理inventory file并与这种方式相结合。
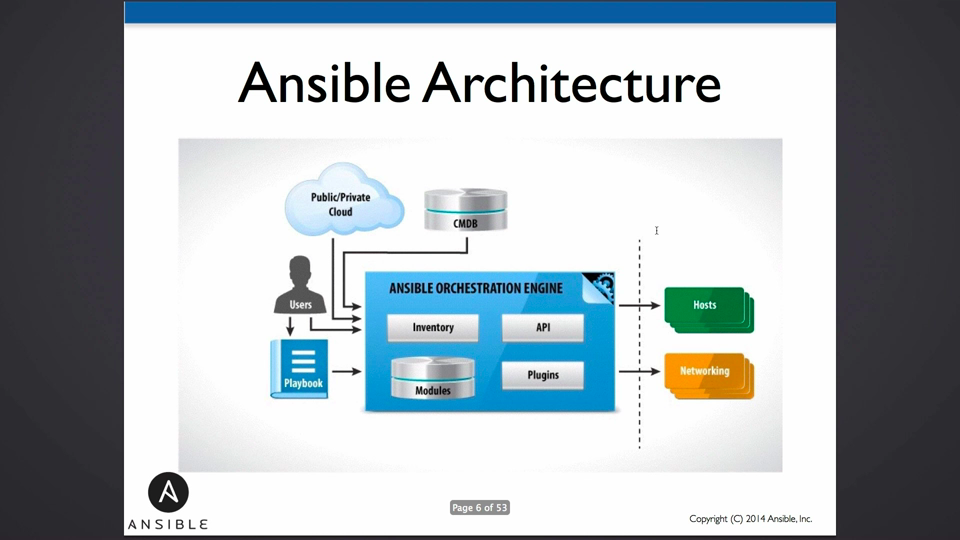
大体上的系统结构(A Big Picture Of Ansible)
一台操作机,直接通过ssh控制一组目标服务器, 目标服务器地址通过ansible的hosts文件内容指定。
+---------------------+
| 目标机器 |
/ +---------------------+
/
+-----------------+ / +---------------------+
| control machine | -----| 目标机器 |
+-----------------+ \ +---------------------+
\
\ +---------------------+
| 目标机器 |
+---------------------+
raw和script模块可以直接允许在目标机器上执行命令和脚本
命令格式(How to cast an ansible command)
$ ansible all -a "/usr/bin/foo" -u username --sudo // ansible [pattern] -m [module] -a [argument] -u [user] $ ansible webservers -m git -a "repo=git://foo.example.org/repo.git dest=/srv/myapp version=HEAD"例如:
$ ansible all -m ping // use current user $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce // as bruce $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce --sudo // as bruce, sudoing to root $ ansible all -m ping -u bruce --sudo --sudo-user batman // as bruce, sudoing to batman
执行一些临时命令(Ad-hoc Commands 2)
http://docs.ansible.com/intro_adhoc.html
常见Modules
- command(默认, 不指定-m参数的时候使用的module)
- 只是执行命令,不会用一些shell下的environment变量等设置
- shell
- 参考command
- copy | file (File Transfer)
ansible atlanta -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/hosts"ansible webservers -m file -a "dest=/srv/foo/b.txt mode=600 owner=mdehaan group=mdehaan"
- git
$ ansible webservers -m git -a "repo=git://foo.example.org/repo.git dest=/srv/myapp version=HEAD"
- service
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd state=started"
Ansible配置(Ansible Configuration)
主要是运行参数的配置, 跟inventory file没有关系, inventory file更多是配置目标机器相关信息, 而ansible配置文件则更多是正规框架行为的调整和配置,比如启动多少并行进程执行命令啦, 执行过程中是否需要交互询问密码啦,等等
ansible的配置可以多种形式进行,生效优先级为:
- ANSIBLE_CONFIG (an environment variable)
- ansible.cfg (in the current directory)
- .ansible.cfg (in the home directory)
- /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
Ansible will process the above list and use the first file found. Settings in files are not merged.
详细配置信息参考http://docs.ansible.com/intro_configuration.html
Playbook
你一定会问,啥是Playbook?
你想啊,部署一个东西的时候, 第一步干啥,第二步执行啥命令,第三步…, 每次都这样手动搞是不是挺烦? 烦就对了, 为了不烦,就得用Playbook这东东: 提前将每次都重复的事情写成式样书, 然后交给ansible-playbook命令去照着执行就可以了!
Playbooks涵盖了配置(Configuration)以及流程(Orchestration)相关规格说明。
Playbook结构
Playbooks contain plays3;
Plays contain tasks4;
Tasks call modules;5
at last, we have handlers6 which can be triggered to be executed after some actions.
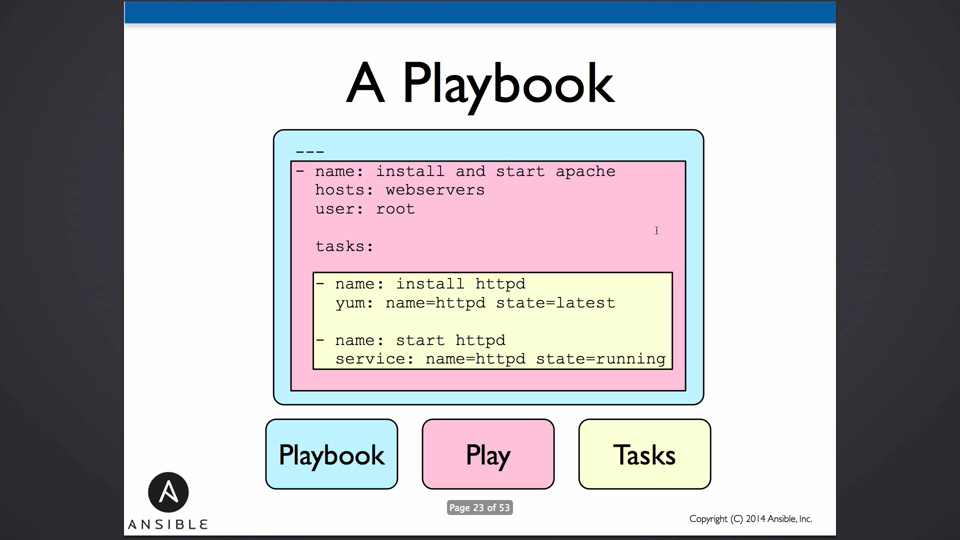
所有plays和tasks按照严格的顺序执行!
下面是一个只有一个play的playbook实例:
---
- hosts: webservers
vars:
http_port: 80
max_clients: 200
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure apache is at the latest version
yum: pkg=httpd state=latest
- name: write the apache config file
template: src=/srv/httpd.j2 dest=/etc/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart apache
- name: ensure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart apache
service: name=httpd state=restarted
内容涵盖了要针对哪些hosts做操作, 定义了哪些变量, 以什么用户执行, tasks有哪些以及handlers有哪些。
--- - hosts: webservers remote_user: yourname sudo: yes sudo_user: postgres
其中, remote_user, sudo等可以存在于play和task两种scope当中。
执行sudo的时候,最好通过命令行指定–ask-sudo-pass参数,否则很可能整个执行过程被挂住(Hang)
Handlers:Running Operations On Change
如果要根据流程中的某些变更做出相应的行为, 可以使用handlers, 即通过定义notify这个action来捕捉事件并做出相应的反应:- name: template configuration file
template: src=template.j2 dest=/etc/foo.conf
notify:
- restart memcached
- restart apache
here is an example of restarting two services when the contents of a file change, but only if the file changes, The things listed in the ‘notify’ section of a task are called handlers.
执行Playbook
Playbook的执行与Ad-hoc Command的执行不同, 后者使用ansible命令, 而Playbook则使用ansible-playbook命令:
$ ansible-playbook playbook.yml -f 10
-f 10表示并行度, 即同样一份playbook,在目标机器集群中一次同时在多少台目标机上执行。
如果想事先了解执行某个playbook会影响到哪些目标机,可以执行:
ansible-playbook playbook.yml --list-hosts
Roles
Roles的概念其实就是组织一系列的tasks啦, handlers啦, vars啦等等到一个以目录为结构实体的组件之中, playbooks可以引用它们。
比如,某项目目录如下:site.yml
webservers.yml
fooservers.yml
roles/
common/
files/
templates/
tasks/
handlers/
vars/
meta/
webservers/
files/
templates/
tasks/
handlers/
vars/
meta/
那么,在某个playbook中,比如site.yml, 可能内容是:
---
- hosts: webservers
roles:
- common
- webservers
另外,我们还可以在roles前后执行相应的tasks:
---
- hosts: webservers
pre_tasks:
- shell: echo 'hello'
roles:
- { role: some_role }
tasks:
- shell: echo 'still busy'
post_tasks:
- shell: echo 'goodbye'
更多Roles或者Playbook实例可以参考http://galaxy.ansible.com/, Ansible Galaxy收录了很多社区贡献的playbooks。
Vars, Conditions, Loops…
写过程序的应该不会陌生啦, 不用废啥嘴皮子了, 基本上是把可以写程序实现的逻辑,改成配置文件里的表达式匹配。
具体细节参考ansible文档
最佳实践
灰度发布
ansible-playbook -i production webservers.yml --limit boston[0-10] ansible-playbook -i production webservers.yml --limit boston[10-20]
总结
即使是使用ansible, 像如何管理部署流程, 如何结合配置和流程, 如何控制发布进度, 如何监控发布情况等等, 依然需要在此基础上进行开发, 这也就是ansible公司又搞了个Ansible Tower的原因,也是很多公司愿意自己开发配置和部署平台的原因。
对于中小企业来说,或许使用现成的工具就可以了,像我大BAT, 基本上都有自己的配置部署平台吧!
参考
Playbook相关参考
- https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_intro.html
- https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_reuse_roles.html
- https://spacelift.io/blog/ansible-playbooks
其它
你想搞哪些机器总得告诉ansible吧,否则它怎么会知道?↩︎
An ad-hoc command is something that you might type in to do something really quick, but don’t want to save for later.↩︎
The goal of a play is to map a group of hosts to some well defined roles, represented by things ansible calls tasks. At a basic level, a task is nothing more than a call to an ansible module, which you should have learned about in earlier chapters.↩︎
The goal of each task is to execute a module, with very specific arguments. Variables can be used in arguments to modules.↩︎
modules are written to be ‘idempotent’ and can relay when they have made a change on the remote system.↩︎
These ‘notify’ actions are triggered at the end of each block of tasks in a playbook, and will only be triggered once even if notified by multiple different tasks.↩︎
开天窗,拉认知,订阅「福报」,即刻拥有自己的全模态人工智能。



